TREATMENTS
VALVULAR HEART DISEASE
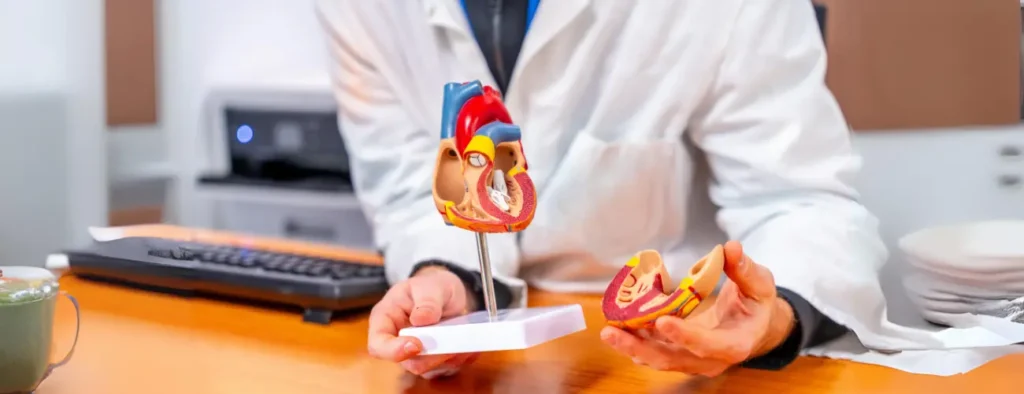
What is Valvular Heart Disease?
Valvular heart disease occurs when one or more of the heart’s four valves doesn’t function properly. These valves control the flow of blood through the heart. When they are damaged or diseased, they may not open or close correctly, leading to various heart problems.
How Does Valvular Heart Disease Happen?
Several factors can contribute to the development of valvular heart disease:
- Congenital heart defects: Some people are born with abnormal heart valves.
- Infections: Conditions like rheumatic fever can damage heart valves.
- Degenerative changes: Valves can wear out over time due to aging.
- High blood pressure and other heart conditions: These can put extra strain on the heart valves.
- Endocarditis: An infection of the heart valves.
Symptoms of Valvular Heart Disease
Symptoms of valvular heart disease often develop gradually and may vary depending on the specific valve affected and the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Chest pain
- Palpitations
- Swelling in the legs and ankles
- Dizziness or fainting
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be associated with other health conditions. If you experience any of these symptoms, consult your doctor for a proper diagnosis.
Prevention of Valvular Heart Disease
While some cases of valvular heart disease cannot be prevented, maintaining good overall heart health can reduce your risk. This includes:
- Regular exercise
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Eating a balanced diet
- Managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Getting vaccinated against infections like rheumatic fever
Treatment Options
Treatment for valvular heart disease depends on the specific valve affected, the severity of the condition, and your overall health. Options may include:
- Medications: To manage symptoms and reduce strain on the heart.
- Lifestyle changes: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
- Catheter-based procedures: Less invasive procedures to repair or replace valves.
- Valve repair surgery: Surgical procedures to repair damaged valves.
- Valve replacement surgery: Replacing a damaged valve with an artificial one.
It’s essential to consult with a cardiologist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific condition.

Om Heart Care is a top-tier cardiac clinic committed to offering heart patients quality and compassionate care. Our clinic was established by renowned interventional cardiologist Dr. Priya Palimkar, who has over twenty years of experience. We are dedicated to providing modern treatments and individualized care.
CONTACT
- +91 9890790780
- info@drpriyapalimkar.com
-
Monday - Saturday
Sunday Closed -
Viman Nagar Clinic
11:00 AM - 02:00 PM
06:00 PM - 09:00 PM
Vishrantwadi Clinic
03:30 PM - 06:00 PM -
Sahyadri Super Speciality Hospital
10:00 AM - 02:00 PM
GET DIRECTIONS
Viman Nagar Clinic
Vishrantwadi Clinic
Sahyadri Super Speciality Hospital
Copyright © 2024. All Rights Reserved | Designed by DIGIOTREE PVT LTD | Disclaimer | Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions

