TREATMENTS
CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE
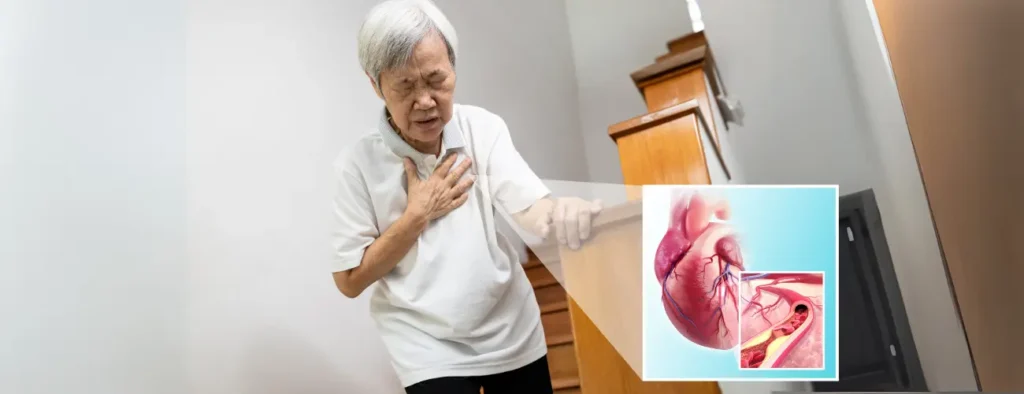
What is Coronary Artery Disease?
Coronary artery disease (CAD) occurs when the arteries that supply blood to your heart become narrowed or blocked by a buildup of plaque. This buildup, called atherosclerosis, reduces blood flow to the heart muscle, potentially leading to chest pain, heart attack, or other heart complications.
How Does CAD Happen?
Atherosclerosis, the underlying cause of CAD, is a gradual process. It begins with the accumulation of fatty substances, cholesterol, and other cellular waste products in the inner walls of your arteries. Over time, these deposits form plaques that can harden and narrow the arteries, restricting blood flow to the heart.
Symptoms of CAD
While CAD often progresses without noticeable symptoms in its early stages, some people may experience:
- Chest pain or discomfort (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Pain in other areas of the body, such as the arms, neck, jaw, or back
- Indigestion-like symptoms
- Sweating
- Nausea
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be associated with other health conditions. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
Prevention of CAD
Many factors contribute to the development of CAD, but adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce your risk. Preventive measures include:
- Regular physical activity
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Eating a balanced diet low in saturated and trans fats
- Managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Managing diabetes
- Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider
Treatment Options
Treatment for CAD depends on the severity of the condition and your overall health. Options may include:
- Lifestyle modifications: Implementing heart-healthy habits like regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management.
- Medications: Various medications can help manage CAD symptoms and reduce the risk of heart attack, including aspirin, beta-blockers, statins, and ACE inhibitors.
- Procedures: Procedures like angioplasty, stent placement, and coronary artery bypass surgery may be necessary to restore blood flow to the heart.
It’s essential to consult with a cardiologist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific condition.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovering from CAD involves a combination of medical care, lifestyle changes, and self-management. Rehabilitation programs can help you regain strength, improve heart health, and reduce the risk of future heart problems.

Om Heart Care is a top-tier cardiac clinic committed to offering heart patients quality and compassionate care. Our clinic was established by renowned interventional cardiologist Dr. Priya Palimkar, who has over twenty years of experience. We are dedicated to providing modern treatments and individualized care.
CONTACT
- +91 9890790780
- info@drpriyapalimkar.com
-
Monday - Saturday
Sunday Closed -
Viman Nagar Clinic
11:00 AM - 02:00 PM
06:00 PM - 09:00 PM
Vishrantwadi Clinic
03:30 PM - 06:00 PM
GET DIRECTIONS
Viman Nagar Clinic
Vishrantwadi Clinic
Copyright © 2024. All Rights Reserved | Designed by DIGIOTREE PVT LTD | Disclaimer | Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions

